Wave and sound
Transverse waves
- Particle moves up and down, perpendicular to the motion of the wave
- Crest: and trough:
- : wave number (m)
info
Wave speed on a string:
- : equilibrium tension of the string
- : mass per unit length of the string
Challenging question
A uniform rope of mass and length hangs vertically from a ceiling. The time it takes for a transverse wave to travel the length of the rope is:
Wave equation for transverse waves
Wave traveling +ve x-direction:
Wave traveling −ve x-direction:
Superposition
If and are incoming wave and reflected wave, their resultant wave
warning
is the speed of a particle, not the wave speed.
Energy in wave motion
- : power of the wave
- : intensity of the wave (W/m)
Reflection of transverse waves
| Fixed boundary | Open boundary |
|---|---|
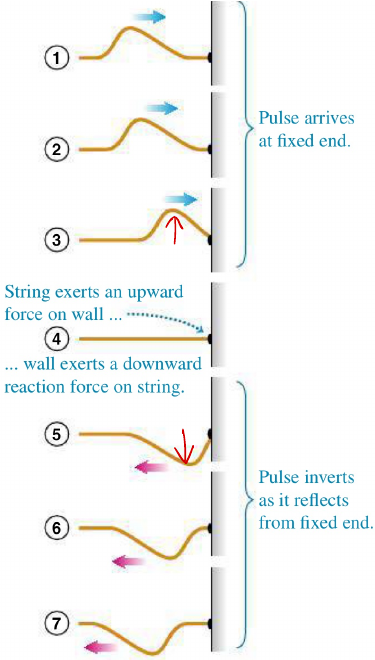 | 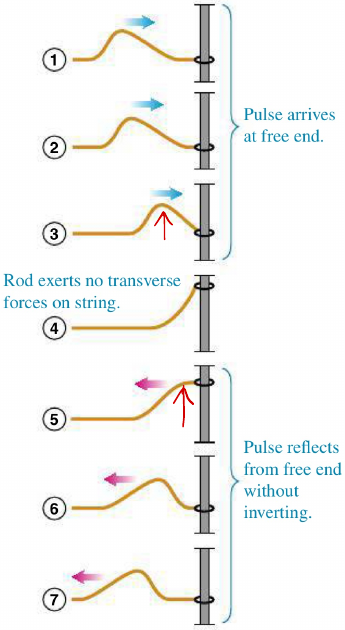 |
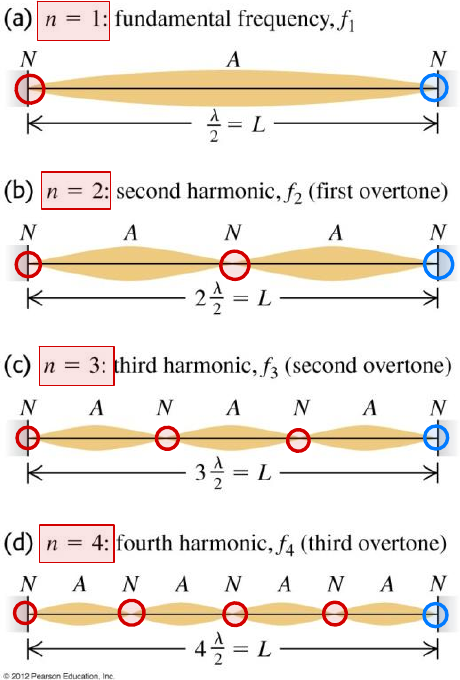
Standing waves
- Node: zero amplitude, destructive interference
- Antinode: maximum amplitude, constructive interference
Harmonics
Fundamental frequency ():
Second harmonic ():
n-th harmonic:
- Length of the string
Sound waves
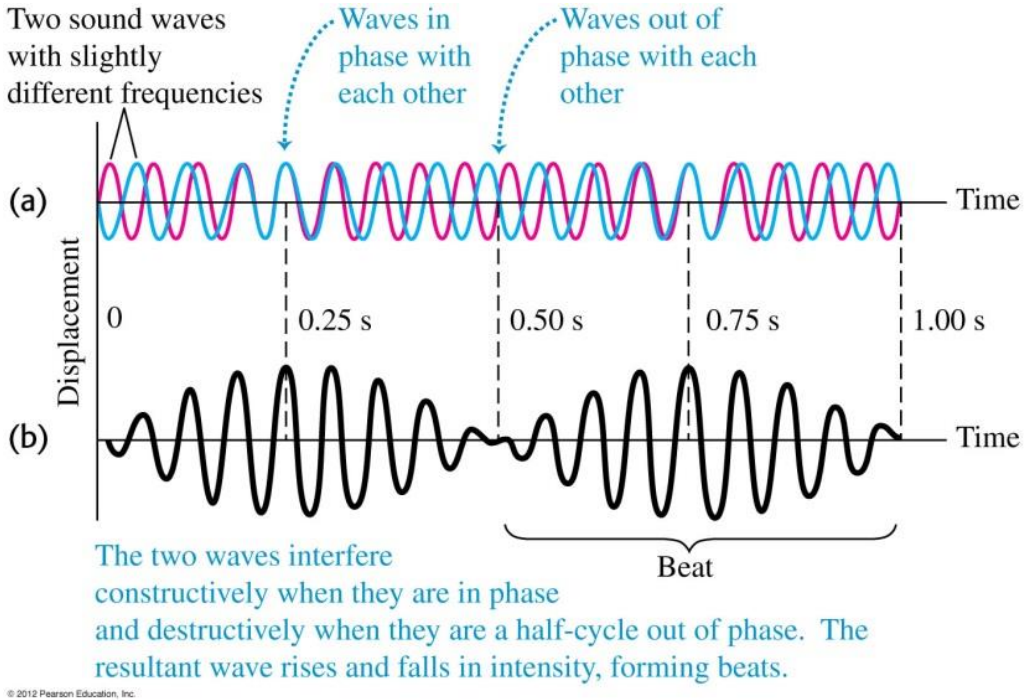
Beats
Superposition of two sound waves
Doppler effect of sound
- : frequency at the listener
- : frequency of the source
- : velocity of the listener
- : velocity of the source
warning
For and : direction pointing from listener to source is positive
e.g. If the listener is approaching the source, while the source is approaching the listener:
Doppler effect of light (out of syllabus?)
where is the relative velocity between the receiver and the source